To take a screenshot of your entire screen, press Command+Shift+3. Press all three keys at once and your Mac’s desktop will flash, you’ll hear a camera sound, and the screenshot will appear on your desktop as a.png file. Take a Screenshot of Part of Your Screen To take a screenshot of part of your screen, press Command+Shift+4 instead. Once you’ve determined which device you would like to use, you can execute the SCREEN command to start the serial terminal session on your Mac. Remember to specify the speed (baud rate) after the device name. Screen /dev/tty.usbserial-FTT3JMUZ 9600. Once you’ve connected, you can use the terminal as you normally would.
If you take a lot of screenshots on a Mac, you might end up with a cluttered desktop. This is because Macs automatically save your screenshots on the desktop. They are also saved as PNG files instead of the more widely used JPEG format. If you want to know how to change where screenshots are saved on a Mac, and the format they are saved in, just follow the steps below:
Where Do Screenshots Go on a Mac?
When you use keyboard shortcuts like Command + Shift + 3, your screenshots are automatically saved to the desktop. You can also right-click the floating thumbnail, which lets you save the screenshot to Documents or Clipboard.
How to Change Where Screenshots are Saved on a Mac

There are two ways to change the defaultscreenshot save directory on a Mac, depending on your operating system. Theeasier way is through the Screenshot app in macOS Mojave. For mac OS HighSierra or earlier, you have to use Terminal, an app for entering commandprompts to control your Mac. Below are the steps for each operating system.
How to Change Where Screenshots are Saved in macOS Mojave or Later
- Go to the Utilities folder and open the Screenshot app. You can also open the Screenshot app by pressing Command + Shift + 5.
- Click Options. The top tile of the menu will show your Save to options:
- Desktop – This is the default setting which saves the screenshot with the following time format: Screen Shot [date] at [time].
- Documents – This will save the screenshot to your Documents folder with the time and date as the file name.
- Clipboard – This will allow you to paste the screenshot to another app which can edit or view images.
- Mail – This lets you compose a new email in the Mail app with the screenshot attached.
- Messages – This will attach the screenshot to a message which you can send to a contact.
- Preview – This will launch Preview, a photo editing app. Your Mac will temporarily name the image file as Untitled until you change it to a different file name.
- Other Location – This will allow you to navigate outside of the locations previously listed to a folder of your choice. You can save to an existing folder or create a new one.
- Choose a Save To option. Your Mac will remember the last one you have selected and will apply this to subsequent screenshots.
How to Change the Default Screenshot Save Location in macOS High Sierra or Earlier
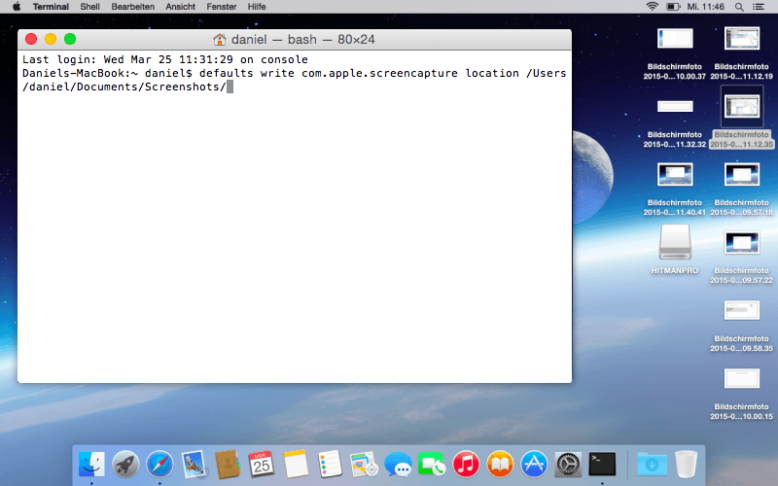
- Open Terminal. You can find the Terminal app in the Utilities folder.
- Type the following command, followed by a space:
Note: Make sure to put a space after the word location, otherwise the command won’t work.
- Drag the folder you want to save to into the Terminal command box. You will see that the file path will now be inserted as another command line in Terminal.
- Press Enter on your keyboard.
- Then type the following command:
- Press Enter or Return. The next time you take a screenshot, it will be saved to the new folder you have created instead of the desktop.
How to Change a Screenshot to JPG and Other File Formats
By default, Macs save screenshots as PNG files, which are usually larger than JPG files. Both can be used for social media, but JPGs are more universally accepted. To save a screenshot as a JPG, use the Terminal to override the default format setting.

- Open Terminal.
- Type the following command, followed by a space: You can also choose to save your screenshots as other formats by default. You can save them as PDF files if you want to edit or open the image in Adobe. You can save them as TIFF files if you want to retain their original image data even after manipulating the image. Or you can save them as GIF files if you want the image to load quickly on the web. Just choose any of the following commands, followed by a space:
Note: Make sure to put a space after the file type, otherwise the command won’t work.
- Hit Enter. The command will be saved to Terminal.
- Test to see if the default option has been changed. Take a screenshot then right-click on the image. Choose Get Info from the contextual menu, then check what is written under “Kind” in the General section.
Once you know how to change the default screenshot settings on your Mac, you’ll be able to customize and improve the way you work with screenshots. Taking a screenshot on a Mac also takes some getting used to, especially for Windows users who are used to hitting the Print Screen key. If you need to improve your screenshot skills, check out our article about how to take a screenshot on a Mac.
Was this article helpful?
Related Articles
This subchapter looks at screencaptures, a Mac OS X-only command.
screencapture creates an image of the screen or a portion of the screen.
from the graphic user interface
The normal method for obtaining a screen capture is through the graphic user interface. Command-Shift-3 takes a screenshot of the screen and saves it as a file to the desktop under the name of “Picture 1” (or next available number if there are already screenshots saved there).
If you have multiple monitors connected, each monitor is saved as a separate picture, named “Picture 1”, “Picture 1(2)”, “Picture 1(3)”, etc.

With Mac OS X 10.6 (Snow Leopard) the default name changes to “Screen shot YYYY-MM-DD at HH.MM.SS XM”, where YYY=year, MM=month, DD=day, HH=hour, MM=minute, SS=second, and XM = either AM or PM.
The basic screen capture options:
- Command-Shift-3: Take a screenshot of the entire screen and save it as a file on the desktop.
- Command-Shift-4, then select an area: Take a screenshot of an area and save it as a file on the desktop.
- Command-Shift-4, then space, then click on a window: Take a screenshot of a selected window and save it as a file on the desktop.
- Command-Control-Shift-3: Take a screenshot of the screen and save it to the clipboard.
- Command-Control-Shift-4, then select an area: Take a screenshot of an area and save it to the clipboard.
- Command-Control-Shift-4, then space, then click on a window: Take a screenshot of a selected window and save it to the clipboard.
In Mac OS X 5 (Leopard) or more recent, the following keys can be held down when selecting an area (with either Command-Shift-4 or Command-Control-Shift-4):
- Space: Used to lock the size of the selected region and move the selected region as the mouse moves.
- Shift: Used to resize only one edge of the slected region.
- Option: Used to resize the selected region with its center as the anchor point.
Different versions of Mac OS X have different default file formats for saving the screenshot:
- Mac OS X 10.2 (Jaguar): jpg
- Mac OS X 10.3 (Panther): pdf
- Mac OS X 10.4 (Tiger): png
changing defaults
The following methods use Terminal to change the default file format and location where the screenshot is saved from the graphic user interface.
In Mac S X 10.4 (Tiger) or more recent, the default screencapture format can be changed in Terminal by using the defaults command. In Mac S X 10.4 (Tiger), the new default does not take effect until you logout and log back in (from the entire computer, not just from Terminal — a full restart will also work) unless you also use the killall command.
$ defaults write com.apple.screencapture type ImageFormat
$ killall SystemUIServer
The ImageFormat can be png (Portable Network Graphic), pdf (Portable Document Format), tiff (Tagged Image File Format), jpg or jpeg (Joint Photographic Experts Group), pict (Macintosh QuickDraw Picture), bmp (Microsoft Windows Bitmap), gif (Graphics Interchange Format), psd (Adobe Photoshop Document), sgi (Silicon Graphics File Format), or tga (Truevision Targe File Format).
JPGs are saved at quality 60%.
To change the default location where the screenshot file is saved (the default is Desktop), use the following Terminal command (where PathName is the full path to a directory.
$ defaults write com.apple.screencapture location PathName
$ killall SystemUIServer
The normal default location would be reset with the following command (where UserName is the current account’s user name.
$ defaults write com.apple.screencapture location /Users/UserName/Desktop
$ killall SystemUIServer
command line screenshots
You can also take screenshots from Terminal.
I needed a screenshot of the CONTROL-TAB selection of a program, but in the graphic user interface, I couldn't simultaneously run Command-Tab and Command-Shift-4, so I used the following command in Terminal to set a 10 second delay and save the screenshot selection:
$ screencapture -T 10 -t png controltab.png
You can add this command to your Mac OS X scripts.
The format is screencapture options filenames. List more than one file name if you have more than one monitor. You can use the options in any combination.
You can use the filename to change the file name from the normal default and to set a relative path to a directory/folder of your choice.
$ screencapture [-icMPmwsWxSCUt][files]
The basic use, which takes an immediate screenshot in the default format and stores it with the designated filename (in this case “Picture1”) in the user’s home directory (not the desktop).
$ screencapture Picture1
Force the screenshot to go to the clipboard (the equivalent of the Command-Shift-Control- choices).
$ screencapture -c [files]
Capture the cursor as well as the screen. This applies only in non-interactive modes (such as a script).
$ screencapture -C [files]
Display errors to the user graphically.
$ screencapture -d [files]
Capture the screenshot interactively by either selection or window (the equivalent of Command-Shift-4). Use the CONTROL key to cause the screenshot to go to the clipboard. Use the SPACE key to toggle between mouse selection and window selection modes. Use the ESCAPE key to cancel the interactive screen shot.
$ screencapture -i [file]
Use the -m option to only capture the main monitor. This does not work if the -i option is also set.
$ screencapture -m [file]
Send the screenshot to a new Mail message.
$ screencapture -M [files]
Use the -o option in window capture mode to only capture the window and to not capture the shadow of the window.
$ screencapture - o [file]
After savng the screenshot, open the screen capture output in Preview.
$ screencapture -P [files]
Use -s to only allow mouse selection mode.
$ screencapture -s [files]
Use -w to only allow window selection mode.
$ screencapture -w [file]
Use -W to start interaction in the window selection mode.
$ screencapture -W [file]
Use the -S option in window capture mode to capture the screen rather than the window.
$ screencapture -S [files]
Set the format with the -t option. The Format can be png (Portable Network Graphic), pdf (Portable Document Format), tiff (Tagged Image File Format), jpg or jpeg (Joint Photographic Experts Group), pict (Macintosh QuickDraw Picture), bmp (Microsoft Windows Bitmap), gif (Graphics Interchange Format), psd (Adobe Photoshop Document), sgi (Silicon Graphics File Format), or tga (Truevision Targe File Format)
Mac Os Terminal Commands
$ screencapture -tFormat[files]
Set a delay time in seconds. The default is five seconds.
$ screencapture -TSeconds[files]
Screen Capture Mac Os Terminal Download
Prevent the playing of sounds (no camera click sound).
$ screencapture -x[files]
Coding example: I am making heavily documented and explained open source code for a method to play music for free — almost any song, no subscription fees, no download costs, no advertisements, all completely legal. This is done by building a front-end to YouTube (which checks the copyright permissions for you).
View music player in action:www.musicinpublic.com/.
Create your own copy from the original source code/ (presented for learning programming).